TQL in tracker reports
You can use TQL syntax in tracker reports “Expert” mode in the search area. Saving a TQL query works the same way as saving a “Normal” mode report.
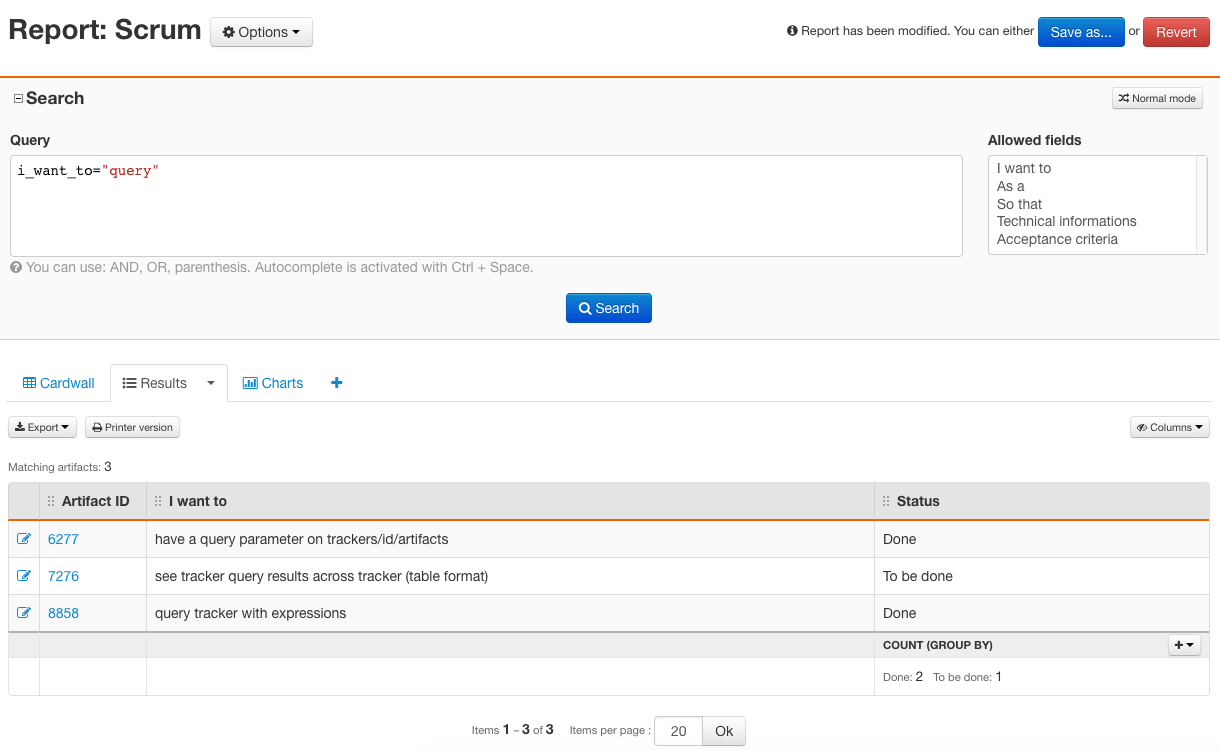
Tuleap Query Language in tracker reports
The goal of TQL is to help you filter very precisely which artifacts you want to see in a tracker report. To achieve this filtering, you can build a query with one or several conditions that artifacts must match in order to be selected. Once selected, artifacts are displayed and you can select which columns you want to see and how to order artifacts with the web user interface, the same way as “Normal” mode reports.
Queries
Note
SELECT, FROM and ORDER BY syntax is not supported in Tracker reports. Please refer to the TQL Limitations table for details about the syntax differences.
Comparison operators
For string, text, files, and @comments:
=,!=For date, integer and float fields:
=,!=,<,<=,>,>=,BETWEEN()For list fields:
=,!=,IN(),NOT IN()
Comparison values
For string, text, and files fields:
string, for example:'text between simple quotes'or"text between double quotes"For integer fields:
integer(3) orstringconvertible to integer (for example:"3")For float fields:
integer(3),float(0.5) orstringconvertible to float (for example:'3.6')For date fields:
NOW()orstringconvertible to date (for example:"2024-10-07")For list fields: matching list values (for example:
"In Review","Ongoing")For list fields bound to users:
MYSELF()orstringuser names (for example:"jdoe","John Doe")For list fields bound to user groups:
stringmatching either the name of a user-defined (“Static”) user group (for example:"Customers") or matching the translated system-defined (“Dynamic”) user group name (for example:"Project members").For @comments:
string
Empty string '' can be used for any field to specify no value.
Dynamic value for date fields: NOW()
start_date > NOW()matches all artifacts where the fieldstart_dateis greater (more recent) than the current time (time when the query is displayed).You can use interval periods with
NOW(), for examplesubmitted_on > NOW() - 1mwill matches all artifacts that have been created during the last month. The supported specificators are:years (
y)months (
m)weeks (
w)days (
d)
Dynamic value for list fields bound to users: MYSELF()
owner = MYSELF() matches all artifacts where the field owner is equal to the current user.
Search in comments
@comments = 'Lorem ipsum'matches all artifacts where at least one follow-up comment contains the stringlorem ipsum. The comparison is case-insensitive.@comments = ''returns the list of artifacts without any comments@comments != ''returns the list of artifacts with at least one comment
When searching in comments, you should be aware of some limitations:
Searches are done for words longer than 3 characters
Some words are not taken into account because they are too common (like
the,a, …)
Search in files
attachment = 'minutes'matches all artifacts where there is at least one attached file with the filename containing “minutes” (for example:"Minutes-20180101.docx") or the description containing “minutes” (for example:"Minutes of last meeting"). The comparison is case-insensitive.
attachment != 'minutes'matches all artifacts where there isn’t any attached files with filename or description containingminutes.
attachment = ''matches all artifacts without any attached files
attachment != ''matches all artifacts that have at least one attached file
Search for linked artifacts
Generic syntax
Artifact links make an oriented graph: you have to specify in which direction the links should be matched with TO or FROM:
Forward links
IS LINKED TOmatches all artifacts that have a link to another artifactIS NOT LINKED TOmatches all artifacts that don’t have a link to another artifact
Reverse links
IS LINKED FROMmatches all artifacts that are linked to by another artifactIS NOT LINKED FROMmatches all artifacts that are not linked to by another artifact
Link type
The query can be refined by specifying the type of the link: WITH TYPE 'my_type'.
For example if you want to target all “fixed in” requests: IS LINKED TO WITH TYPE 'fixed_in'.
Origin & destination
Origin or destination can also be specified: to match an artifact ARTIFACT = 123, a tracker TRACKER = 'epic', or a different tracker TRACKER != 'epic'.
IS LINKED FROM ARTIFACT = 123matches all artifacts that are linked to by the artifact #123.IS LINKED TO TRACKER = 'release' WITH TYPE 'fixed_in'matches all artifacts that are “fixed in” an artifact ofreleasetracker.IS LINKED TO TRACKER != 'release' WITH TYPE 'fixed_in'matches all artifacts that are “fixed in” an artifact other thanreleasetracker.
Query aliases
Some builtin types are not easy to express/understand (hello _is_child 👋) so TQL offers some aliases for better expressiveness of the query.
Search for parent relationship
WITH PARENTmatches all artifacts that have a parent artifact (alias ofIS LINKED FROM WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITHOUT PARENTmatches all artifacts that don’t have a parent artifact (alias ofIS NOT LINKED FROM WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITH PARENT ARTIFACT = 123matches all artifacts that have artifact #123 as a parent (alias ofIS LINKED FROM ARTIFACT = 123 WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITHOUT PARENT ARTIFACT = 123matches all artifacts that don’t have artifact #123 as a parent (alias ofIS NOT LINKED FROM ARTIFACT = 123 WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITH PARENT TRACKER = 'epic'matches all artifacts that have an artifact from trackerepic(regardless of the project) as a parent (alias ofIS LINKED FROM TRACKER = "epic" WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITHOUT PARENT TRACKER = 'epic'matches all artifacts that don’t have an artifact from trackerepic(regardless of the project) as a parent (alias ofIS NOT LINKED FROM TRACKER = "epic" WITH TYPE '_is_child')
Search for children relationship
WITH CHILDRENmatches all artifacts that have a least one child artifact (alias ofIS LINKED TO WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITHOUT CHILDRENmatches all artifacts that don’t have a child artifact (alias ofIS NOT LINKED TO WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITH CHILDREN ARTIFACT = 123matches all artifacts that have artifact #123 as a child (alias ofIS LINKED TO ARTIFACT = 123 WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITHOUT CHILDREN ARTIFACT = 123matches all artifacts that don’t have artifact #123 as a child (alias ofIS NOT LINKED TO ARTIFACT = 123 WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITH CHILDREN TRACKER = 'task'matches all artifacts that have an artifact from trackertask(regardless of the project) as a child (alias ofIS LINKED TO TRACKER = "epic" WITH TYPE '_is_child')WITHOUT CHILDREN TRACKER = 'task'matches all artifacts that don’t have an artifact from trackertask(regardless of the project) as a child (alias ofIS NOT LINKED TO TRACKER = "epic" WITH TYPE '_is_child')
Note
You can use both CHILD and CHILDREN in queries to better suit your taste:
WITH CHILDREN ARTIFACT = 123 is the same than WITH CHILD ARTIFACT = 123
Search for test coverage
Looking for test coverage is another common use case that benefits of a dedicated syntax:
IS COVEREDmatches all artifacts (eg: user stories) that are covered by tests (alias ofIS LINKED TO WITH TYPE '_covered_by')IS COVERED BY artifact = 123matches all artifacts (eg: user stories) that covered by test 123 (alias ofIS LINKED TO ARTIFACT = 123 WITH TYPE '_covered_by')IS NOT COVEREDmatches all artifacts (eg: user stories) that are not covered by any test (alias ofIS NOT LINKED TO WITH TYPE '_covered_by')IS COVERINGmatches all artifacts (eg: tests) that are covering other artifacts (eg: user stories) (alias ofIS LINKED FROM WITH TYPE '_covered_by')IS COVERING artifact = 123matches all artifacts (eg: tests) that are covering artifact (eg: user story) 123 (alias ofIS LINKED FROM ARTIFACT = 123 WITH TYPE '_covered_by')IS NOT COVERINGmatches all artifacts (eg: tests) that doesn’t cover any other artifacts (eg: user stories) (alias ofIS NOT LINKED FROM WITH TYPE '_covered_by')
Query construction
You can assemble your different comparisons with logical operators AND and OR and use parenthesis () to force precedence.
Query example:
(summary = "soap" OR summary = "rest")
AND description = "documentation" AND story_points BETWEEN(3, 8)
Note
Be careful, you must use the name of fields and not the label to construct queries.
Sending the query to the server can produce the following errors:
The query syntax is incorrect (for example: if you forget a closing quote
")The name used in a comparison doesn’t match any existing field name (or there is a mistake in the name)
The value is not defined for the list field (for example:
assigned_to = "non_existent_user")The dynamic value is not supported for this field (for example:
text_field = NOW())The comparison operator is not supported for this field (for example:
list_field >= 3)The empty value is not allowed for this comparison (for example:
date_field BETWEEN("", "2017-01-18"))The query uses
MYSELF()and the current user is not logged in (for example: when browsing a Tuleap platform as an anonymous user)The field type is unsupported
The query is too complex
Important
The query is too complex when it exceeds a limit. This limit is defined by Site Administrators on Site Administration > Tracker > Report.
Pro tips
For a better usability in building query, Tuleap provides syntax highlighting
and auto-completion (ctrl+space on field names).
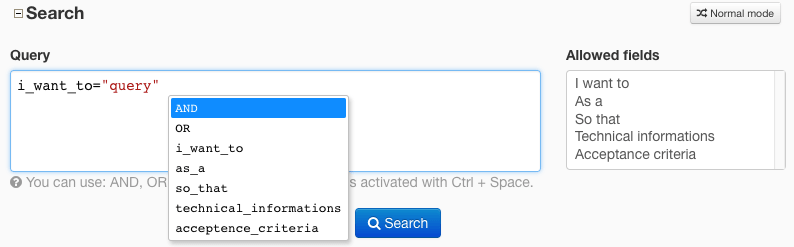
Highlighting and auto-completion
Moreover, in order to help you find out which fields you can use for comparisons, there is a select box with all allowed fields. If you click on one of them, the field’s name is added to the query.
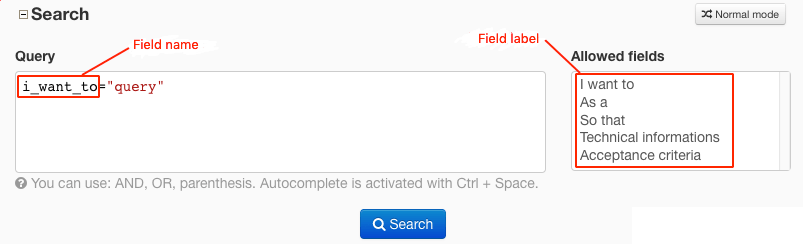
Allowed fields
Date operators
When searching on date fields using TQL, you should be aware of the sometimes subtle differences between the various operators. We have found this diagram helpful. Here, we use all available operators supporting date fields and a given date (“2017-01-18”) and represent the period that will be selected as a result. For example, date_field > "2017-01-18" means date_field is later than 2017-01-18 23:59:59, while date_field >= "2017-01-18" means date_field is later than or equal to 2017-01-18 00:00:00
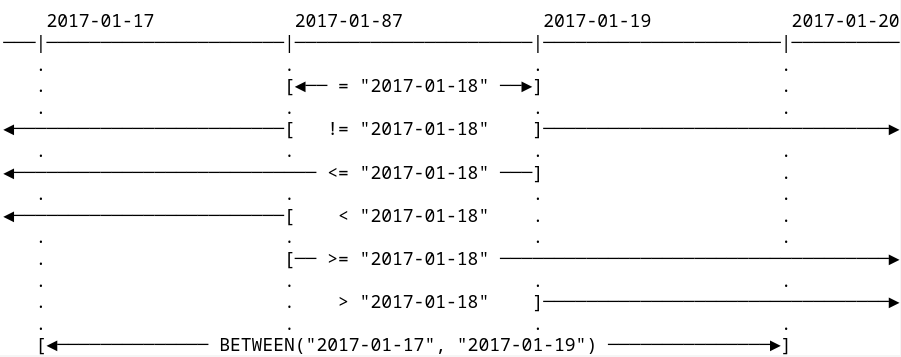
Explanation of date operators
